
As you consider the safety and quality of your drinking water in India, the terms ‘RO’, ‘UV’, ‘UF’, and ‘TDS’ often come into play. Each represents a distinct purification technology incorporated within modern water purifiers to ensure your water is safe to consume. But what exactly is RO UV UF TDS in a water purifier? Let’s demystify these acronyms.
Reverse Osmosis (RO) utilises a semipermeable membrane to remove larger particles and dissolved impurities. Ultraviolet (UV) purification deploys UV light to kill bacteria and viruses without altering water’s chemical composition. Ultrafiltration (UF), similar to RO, filters out suspended solids but works without electricity, and finally, TDS indicators measure the Total Dissolved Solids in your water, highlighting its overall purity.
Understanding these technologies is crucial as they form the foundations of the water purification system. The combination used, whether a single method or an integrated approach involving multiple types of water purifiers, can significantly affect the water purification process and the quality of water you drink.
Key Takeaways
- RO is known for removing larger particles and dissolved substances, ensuring purity at a molecular level.
- UV technology leverages light to sterilise water, targeting harmful pathogens efficiently.
- UF offers a gravity-based filtration solution, excellent for removing suspended solids.
- TDS levels in water indicate the concentration of dissolved impurities.
- Selecting the right type of water purifier involves understanding these individual technologies and their role within your water purification system.
RO Vs UV Vs UF in Water Purifiers
RO, UV, and UF are the 3 most common water purification technologies on the market. Each has their purpose and what they are best for.
Below we’re going to compare these 3 purification methods in an RO vs. UV vs. UF side-by-side comparison.
RO (Reverse Osmosis)
- Best for high TDS water
- Removes dissolved salts
- Requires electricity
- Produces wastewater
UV (Ultraviolet)
- Best for low TDS water
- Kills bacteria and viruses
- Requires electricity
- No wastewater
UF (Ultrafiltration)
- Works without electricity
- Removes bacteria and cysts
- Not able to extract dissolved salts.
- No wastewater
The Significance of Water Purification Technology
In India, access to safe drinking water remains a pressing concern, and water purification technology has emerged as an indispensable ally. This section emphasises the crucial role that such technology plays in delivering purified water to millions of households. When comparing different water purifier systems, it becomes evident – that water purification is not merely a convenience but a vital necessity. Whether it’s through filtration, chemical treatment, or advanced processes, these technologies strive to purify water, making it safe for consumption.
Untreated water poses a multitude of health risks, where contaminants ranging from bacteria to heavy metals threaten well-being. It is the advancement in water purification that combats these risks, and here, you’ll understand how. The comparison among water purifiers isn’t just about price and brand but also about the efficiency and effectiveness with which they can remove impurities and render water potable.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems remove dissolved salts and impurities.
- UV filters use ultraviolet radiation to eliminate pathogens.
- Ultrafiltration (UF) purifiers trap and remove microorganisms and suspended solids.
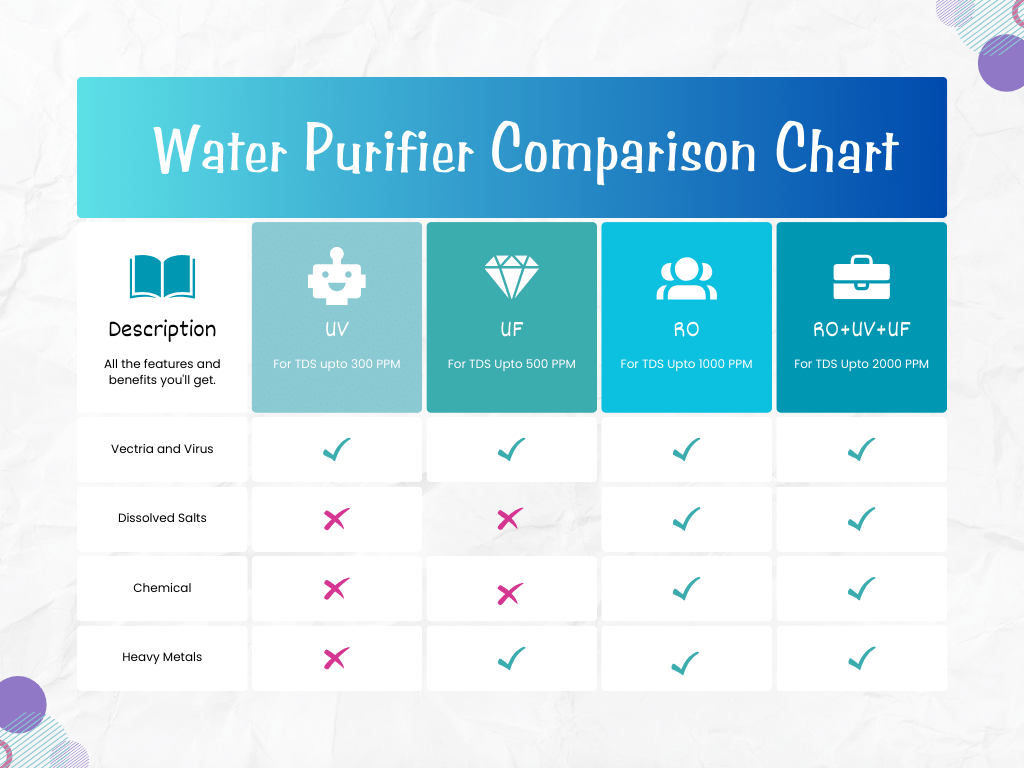
The breadth of water purifier comparison charts reveals a spectrum of choices suited to different needs – ranging from simple particulate filters to sophisticated RO+UV+UF systems. One must understand that not every purifier is built the same, nor are all sources of water identical in their contamination. Hence, making an informed decision on which water purifier to invest in is paramount for ensuring the health and safety of your family.
The below table represents the efficacy of various water purification techniques with respect to common contaminants.
| Contaminant | RO Purification | UV Purification | UF Purification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria and Viruses | Effective | Effective | Effective |
| Dissolved Salts | Highly Effective | Not Effective | Not Effective |
| Heavy Metals | Effective | Not Effective | Moderately Effective |
| Suspended Solids | Effective | Effective | Highly Effective |
Exploring RO Water Purifiers: How Does Reverse Osmosis Work?
Utilising a complex process known as reverse osmosis, these devices are instrumental in ensuring that the water you drink is free from a variety of contaminants.
Core Components of an RO Water Purification System

The backbone of any RO system is its RO membrane, a semi-permeable barrier designed to let water molecules pass while blocking larger particles, like dissolved salts and impurities. The process begins when high pressure forces the water across this membrane, leaving unwanted substances behind which are then flushed away. Additionally, the system includes sediment filters and carbon filters to remove particulates and chlorine which could harm the delicate RO membrane.
Benefits of RO Filtration for Safe Drinking Water
The implementation of reverse osmosis in water purification yields numerous benefits. It effectively removes various contaminants, such as pesticides, nitrates, sulfates, fluoride, bacteria, and viruses, and ensures cleaner and safer drinking water. This is a good option in places where such pollutants frequently dissolve in the water supply.
- Reduces the risk of consuming harmful chemicals and microorganisms
- Improves the taste and odour of the water by removing dissolved impurities
- Provides a reliable source of pure water for homes and industries
Understanding Reverse Osmosis Membrane Function
The success of an RO system revolves principally around the multifaceted RO membrane. It’s fascinating to realise that this component is capable of filtering particles down to 0.0001 microns. The filtration efficacy turns it into an impenetrable fortress against contaminants, which are otherwise unable to be seen or tasted, yet are detrimental to health. Regular maintenance and occasional replacement of the RO membrane ensure optimal performance, fulfilling its purpose of producing pristine, potable water.
What is a UV Water Purifier and Its Function in Water Purification?
Understanding the critical role of a UV water purifier in the domain of water filtration is pivotal for ensuring the safety of the water you consume. Utilising a powerful form of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, these purifiers serve an essential function—disinfecting your water by effectively destroying harmful microorganisms without introducing any chemical changes to the water’s taste or odour.
While considering water filtration solutions, it’s important to realise how ultraviolet purifiers work. As water passes through the system, it is exposed to ultraviolet light. This UV radiation is highly effective at deactivating bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens by disrupting their DNA and rendering them harmless—providing a chemical-free method to disinfect water from contaminants that could potentially lead to waterborne diseases.
- Chemical-Free Disinfection: Unlike traditional methods that rely on chlorine or other chemicals, UV purification maintains the natural composition of water.
- Efficient Process: The process of disinfection is quick and efficient, ensuring water is safe to drink within seconds of treatment.
- Eco-Friendly: UV purifiers are environmentally friendly, with no byproducts or waste, making them a sustainable choice for safe water.
Diving Into UF Water Purifiers and Their Mechanism
When you’re in the market for a water purifier, you’ll likely come across the term ultrafiltration (UF) quite frequently. The UF in the UF water purifier stands for ultrafiltration. This sophisticated process utilises a hollow fibre threaded membrane to remove suspended solids from your water, offering a robust solution to purifying your drinking water. Let’s break down the ultrafiltration method and see why it’s a top choice for eliminating impurities.
Key Features of Ultrafiltration (UF) Technology
The important aspect of UF technology lies in its membrane. The term UF full form relates to a barrier that effectively separates harmful microorganisms and suspended particles from your water. Unlike microfiltration, which targets relatively larger particles, UF can suspend and retain much smaller elements due to its finer membranes. A key component in these UF systems is the hollow fibre threaded membrane, which provides a large surface area for water to pass through, enabling effective purification.
Comparison Between UF and Other Purification Methods
- UF vs. RO: While Reverse Osmosis (RO) removes dissolved salts, UF is selective, primarily targeting suspended solids and pathogens.
- UF vs. UV: Unlike UV purification which disinfects water by exposing it to ultraviolet light, UF physically blocks contaminants with its membrane.
- UF vs. Sediment Filters: Sediment filters trap larger particles, whereas UF captures finer particles and microbes.
The Role of UF in Removing Microorganisms
Ultrafiltration stands out in its ability to address contaminants that are too small for the naked eye. Its role in removing microorganisms is vital, especially in areas where waterborne diseases are prevalent. The UF water purifier’s technique of employing a semi-permeable membrane ensures a barrier against bacteria and viruses, safeguarding your family’s health without the need for chemical additives.
Deciphering TDS in Water Purifiers: Total Dissolved Solids Explained
When we talk about the water quality in your home, the term ‘TDS’, which stands for Total Dissolved Solids, frequently comes into play. This measurement is pivotal in assessing the purity of your water by indicating the concentration of dissolved solids present. But what exactly are these solids? They include a variety of minerals, salts, metals, and cations that are dissolved in water. Confused about TDS levels? Let’s simplify it; the TDS level indicates how many milligrams of these substances are present in a litre of water.

Understanding the implications of TDS can be crucial for your health and the longevity of your water purifiers. A higher TDS level means more ions and substances, such as dissolved salts and minerals, which aren’t necessarily harmful but can affect the taste, smell, and overall water quality. In contrast, very low TDS levels can result in flat-tasting water, lacking in essential minerals beneficial for the body.
| TDS Level (mg/L) | Description | Water Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Less than 300 | Excellent | High quality, great taste |
| 300 – 600 | Good | Suitable for consumption |
| 600 – 900 | Fair | Acceptable, but not ideal for consumption |
| 900 – 1200 | Poor | Unpleasant taste, possibly unhealthy |
| More than 1200 | Unacceptable | Unsuitable for drinking |
Why is monitoring TDS in water purifiers essential? A primary reason is that dissolved solids which are too high can lead to the inefficiency of soaps and detergents due to a decrease in their solubility, and can also contribute to a build-up of scale in pipes and boilers. Water purifiers with TDS controllers or Mineralizers help in maintaining this balance, making sure that the TDS levels are within an acceptable range, thereby ensuring the water quality is optimal for your use.
- Dissolved salts and minerals contribute to TDS
- Visible sediments or cloudiness are not included in TDS
- Low TDS is not always indicative of healthy water
- Water purifiers regulate TDS for better health and efficiency
Tackling Hard Water: The Integration of RO, UV, and UF Technologies
When you’re faced with the challenge of hard water in your household, the culprits are typically high levels of minerals like calcium and magnesium dissolved in water. Not only can these minerals cause scaling and hinder the efficiency of your appliances, but they can also affect your skin and hair quality. Thankfully, modern water purifiers are designed to convert hard water to soft water, improving it for both consumption and usage.
What Makes Water ‘Hard’ and How Purifiers Address It
Hard water is characterised by its elevated mineral content, acquired as it percolates through limestone and chalk deposits. To tackle this issue, a comprehensive filtration system, combining RO (Reverse Osmosis), UV (Ultraviolet), and UF (Ultrafiltration) technologies, is employed to efficiently remove these excess minerals, rendering the water effectively ‘soft’. This cutting-edge integration ensures that the water is not only safe for consumption but also gentler in its interaction with your domestic life.
Transforming Hard Water into Soft Water: The Process
The transformation process of hard water into soft water is a meticulous one. Reverse Osmosis technology plays a pivotal role by forcing water through a semi-permeable membrane, leaving behind the dissolved minerals. UV purification adds an extra layer of security by using ultraviolet light to kill any microbiological contaminants that may have passed through the RO membrane. Lastly, UF employs a hollow fibre threaded membrane, capturing any suspended solids that may remain. These technologies work in synergy to produce soft, purified water that benefits your health and home.
| Technology | Function | Benefits of Addressing Hard Water |
|---|---|---|
| RO (Reverse Osmosis) | Removes dissolved minerals by pushing water through a semi-permeable membrane | Significantly reduces mineral content, prevents scaling |
| UV (Ultraviolet) | Disinfects water using UV light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens | Enhances purity by ensuring microbial safety |
| UF (Ultrafiltration) | Uses a hollow fibre membrane to trap suspended solids, bacteria, and viruses | Supports RO in removing contaminants and fine particulate matter |
What is RO UV UF TDS in a Water Purifier?
When you ponder over the technologies powering modern water purifiers, several abbreviations emerge: RO (Reverse Osmosis), UV (Ultra Violet), UF (Ultrafiltration), and TDS (Total Dissolved Solids). Each plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the water you drink is devoid of impurities. In this section, I will show you how these technologies converge to create a comprehensive purification system.
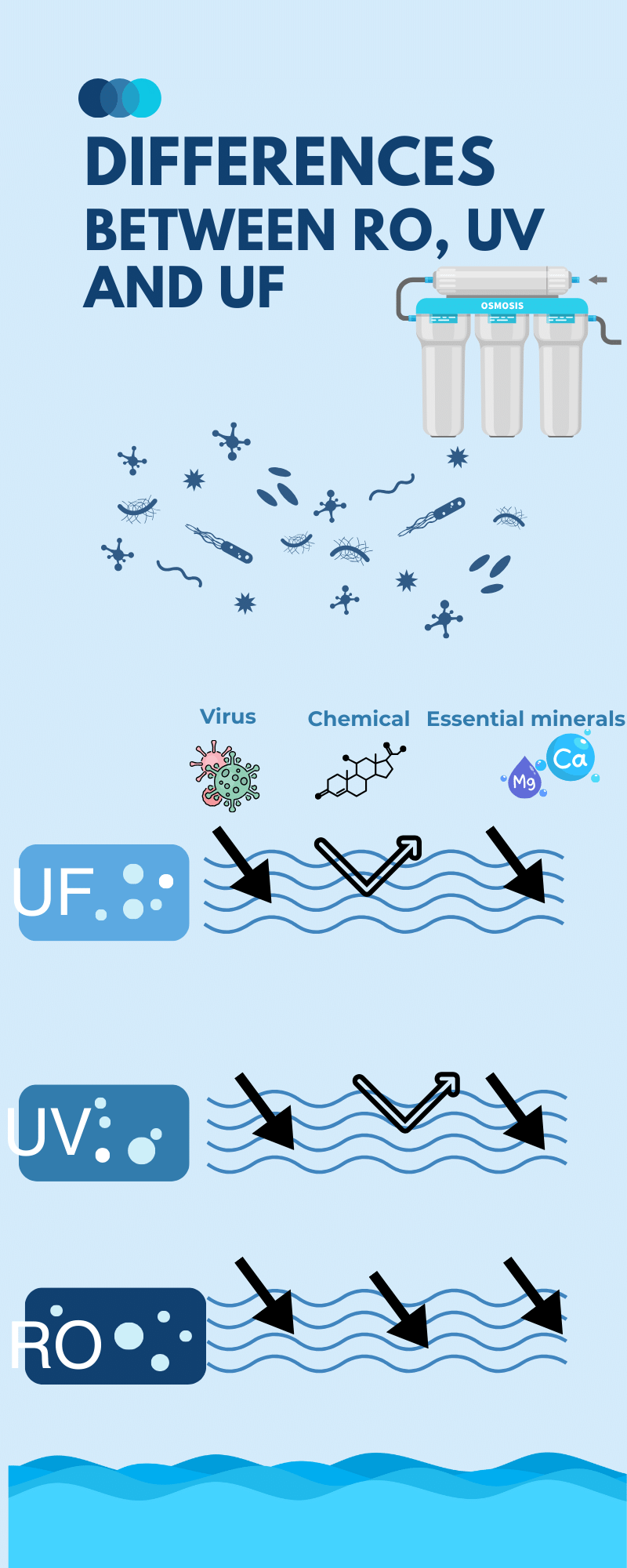
The RO vs UV vs UF debate centres on the differing methods each technology employs to purify water. Reverse Osmosis forces water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing contaminants down to a molecular level. UV purification passes water under ultraviolet light, neutralising viruses and bacteria without altering the water’s chemistry. UF involves passing water through a myriad of hollow fibres, trapping various impurities on the surface.
Conversely, TDS measurement gauges the total dissolved solids in water, a key indicator of water quality. While tenuous particles can pass through UV and UF, RO filters are capable of reducing TDS significantly. Here’s a comparison that details the unique capabilities of these technologies:
| Technology | Contaminant Addressed | Purification Process | Impact on TDS |
|---|---|---|---|
| RO | Dissolved salts, metals, impurities | Water is forced through an RO membrane, removing contaminants. | Significant reduction |
| UV | Bacteria, viruses | UV light disrupts the DNA of microorganisms, eliminating them. | No impact on TDS |
| UF | Suspended solids, some bacteria | Water passes through microscopic pores, blocking larger particles. | No impact on TDS |
Understanding the distinction between RO UV UF TDS in water purifier technology. While each has its strengths, the combination of RO, UV, and UF safeguards against a wide spectrum of impurities, ensuring that your drinking water is safe and palatable.
- RO is particularly effective for treating hard water, ridding it of dissolved minerals.
- UV is your shield against microbial threats, efficiently neutralising germs.
- UF excels in removing colloidal particles without the need for electricity.
Choosing the Right Water Purifier: Factors to Consider
Securing the right water purifier for your household necessitates a comprehensive understanding of your current drinking water quality and the specific impurities from the water to be addressed. By carefully analysing your water supply and identifying the levels of possible contaminants, you can tailor your selection to fit your needs precisely.
Analysing Water Supply Quality and Contaminant Levels
Before you decide on a water filter, it’s essential to examine the quality of your water supply. Look for a comprehensive water analysis report or consider conducting a water test. This will give insight into what kinds of water purifiers would be most effective by revealing critical details about the contaminant levels in your water supply.
Understanding Water Purifier Comparisons: RO vs UV vs UF
Water filters come in various types, each equipped to remove certain impurities from the water. Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems excel at reducing dissolved salts and minerals, Ultra Violet (UV) purifiers are adept at neutralising microorganisms, and Ultrafiltration (UF) purifiers can remove larger particles suspended in water. An understanding of what each technology offers allows you to make an informed decision on the right water purifier for your home.
| Technology | Contaminants Removed | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| RO (Reverse Osmosis) | High TDS, heavy metals, and dissolved salts | Areas with hard water supply |
| UV (Ultra Violet) | Bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens | Water with biological impurities |
| UF (Ultrafiltration) | Suspended solids, bacteria, and some viruses | Murky water sources with high microorganism content |
Real-World Impacts: Case Studies on Water Purifier Technologies
As I explore the tangible benefits of water purification systems, it’s crucial to consider their real-world impacts. These effects are not limited to laboratory settings; they extend to practical applications in both urban and rural communities.
Examples of Effective TDS Removal in Urban and Rural Settings
Urban areas, grappling with industrial contamination, and rural regions, facing natural water hardness, both require efficient Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) management. In New Delhi, a study showcased how water purifiers equipped with RO technology substantially reduced TDS levels, leading to safer drinking water. Contrastingly, in a rural village of Rajasthan, a solar-powered desalination unit has been instrumental in purifying brackish water for agricultural and drinking purposes, indicating the adaptability of water purification strategies to diverse environments.
The Efficacy of Combined Purification Technologies
When evaluating water purification technologies, the combination of RO, UV, and UF has been resoundingly successful. A comparative study in Mumbai highlights this synergy. Post-monsoon, the water quality is significantly compromised, but integrated systems have proven adept at ensuring consistent water purity irrespective of seasonal changes. This underlines the efficacy of multi-faceted water purification approaches for urban water purification and the potential adaptability for rural water purification scenarios.
| Location | Challenges | Technology Used | TDS Level Before | TDS Level After |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Delhi | Industrial wastes | RO purifiers | 900 ppm | 50 ppm |
| Rajasthan | Brackish groundwater | Solar desalination | 2000 ppm | 500 ppm |
| Mumbai | Sewage contamination post-monsoon | RO+UV+UF purifiers | 750 ppm | 120 ppm |
Conclusion
My exploration into the multifaceted world of water purification, I’ve unveiled the critical technologies that safeguard your drinking water—RO, UV, UF, and TDS—each serving a distinctive role in the pursuit of water safety. Through intricate processes and advanced engineering, these systems are pivotal in ensuring water is effective for consumption. As potential hazards lurk unseen in unfiltered water, understanding these methods becomes vital for maintaining your health and well-being.
The journey through various purification technologies illustrates the complexity and importance of effective water purification. From the imperative removal of sediments and salts to the neutralisation of harmful microorganisms, every measure contributes to your access to clean, salubrious water. It’s imperative to recall the salient points that emerge when choosing a water purifier, such as the characteristics of your water supply and contaminant levels present.





